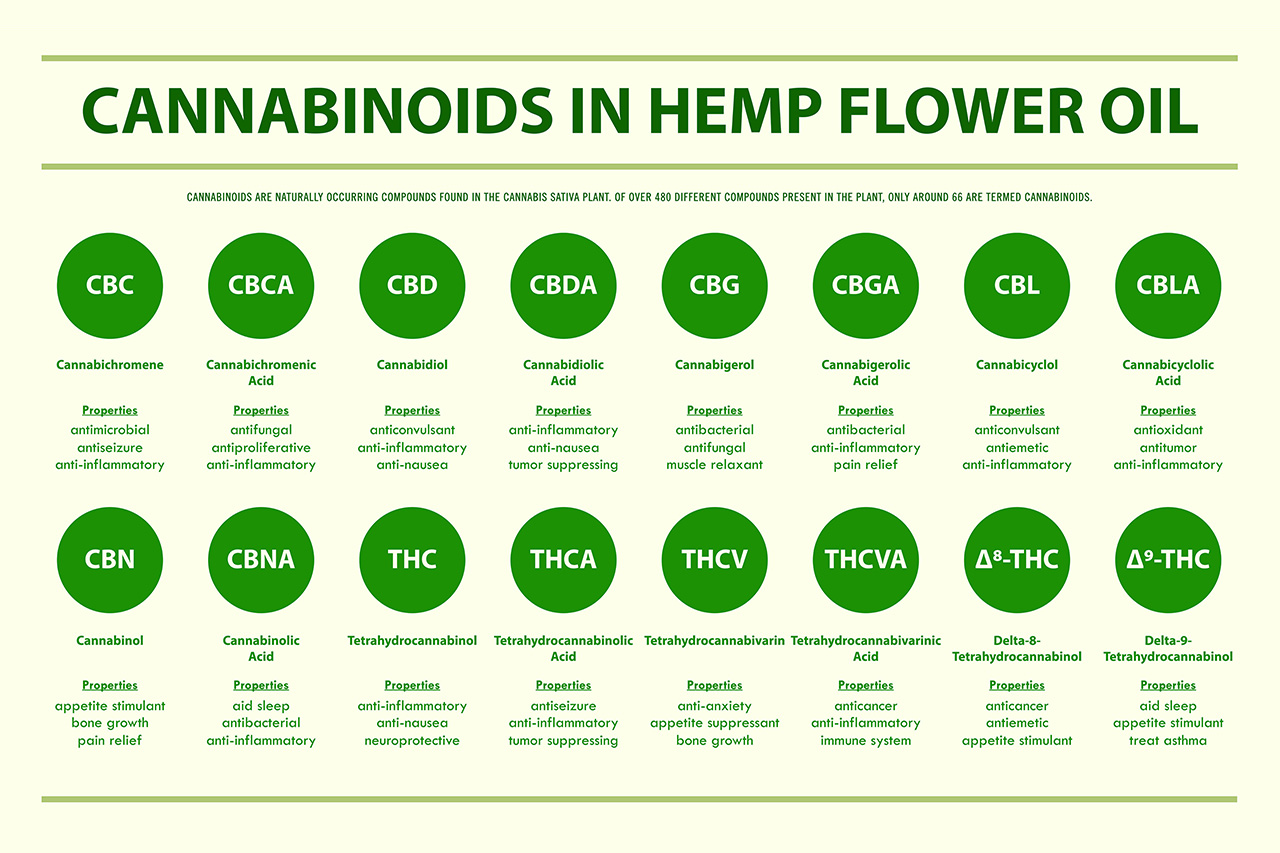
Do You Know Your Main Cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are a group of chemical compounds that are found in the cannabis plant. These compounds interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, which is responsible for regulating a range of physiological processes, such as pain, mood, appetite, and sleep.
There are over 100 different cannabinoids that have been identified in the cannabis plant, each with its own unique properties. Cannabinoids are chemical compounds that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce a range of effects. Some of the most well-known cannabinoids include Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
The Most Well-Known Cannabinoids: THC & CBD
THC is the most well-known and commonly found cannabinoid in cannabis. It is responsible for the psychoactive effects of marijuana, such as euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception of time and space. THC works by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and nervous system, producing a range of effects on the body and mind.
CBD, on the other hand, is non-psychoactive and does not produce a “high” or euphoric feeling. Instead, CBD has been reported to produce a range of potential therapeutic effects, such as reducing inflammation, relieving anxiety, and improving sleep.
Other Common Cannabinoids:
Other cannabinoids found in cannabis include delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta-8-THC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THC-A), and tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). Each of these cannabinoids has its own unique properties and potential therapeutic uses.
Delta-8, delta-9, and delta-10 THC are all different chemical variations of tetrahydrocannabinol, which is the primary psychoactive component of cannabis.
Delta-9 THC is the most well-known and commonly found in cannabis, while delta-8 THC is a less abundant cannabinoid that is present in smaller quantities in cannabis plants. Delta-10 THC is even less commonly found in cannabis and is typically produced through chemical conversion from other cannabinoids.
Research into Therapeutic Values of Cannabinoids:
Research on cannabinoids is still in its early stages, but there is growing evidence to suggest that these compounds may have potential therapeutic applications for a range of health conditions, such as chronic pain, anxiety, depression, and epilepsy.
In addition to their potential therapeutic uses, cannabinoids have also been shown to have potential recreational uses. Cannabis is often used for its psychoactive effects, and many people use marijuana for its relaxing and euphoric effects.
The Most 8 Common Cannabinoid Compounds:
CBD:
Cannabidiol, or CBD, is another well-known cannabinoid found in cannabis. Unlike delta-9-THC, CBD is non-psychoactive, meaning it does not produce a “high” or euphoric feeling. Instead, CBD has been reported to produce a range of potential therapeutic effects, such as reducing inflammation, relieving anxiety, and improving sleep. CBD works by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce its effects.
CBG:
Cannabigerol, or CBG, is a minor cannabinoid found in cannabis that is believed to have potential therapeutic effects. CBG has been reported to have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as potential uses in the treatment of glaucoma and cancer. CBG works by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce its effects.
CBN:
Cannabinol, or CBN, is a minor cannabinoid found in aged cannabis plants. CBN is believed to have sedative and analgesic properties, and it has been reported to produce a calming effect on the body and mind. CBN works by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce its effects.
Delta-8-THC:
Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol, or Delta-8-THC, is a minor cannabinoid found in cannabis plants. It is structurally similar to delta-9-THC — however, delta-8-THC is less potent than delta-9-THC and has been reported to produce a milder high. Delta-8-THC is often used as a legal alternative to delta-9-THC, as it is currently not explicitly listed as a controlled substance in some jurisdictions.
Delta-9-THC:
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or delta-9-THC, is the most well-known and commonly found cannabinoid in cannabis. It is the primary psychoactive component, and it is responsible for the “high” or psychoactive effects – such as euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception of time and space that are often associated with marijuana use. Delta-9-THC works by binding to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and nervous system, producing a range of effects on the body and mind.
Delta-10-THC:
Delta-10-tetrahydrocannabinol, or delta-10-THC, is a rare cannabinoid that has been recently discovered and is still being studied. It is believed to have similar effects to delta-8 and delta-9 THC, although more research is needed to understand its effects and potential therapeutic uses.
THC-A:
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, or THC-A, is the non-psychoactive precursor to delta-9-THC that is found in raw cannabis plants. THC-A is converted into delta-9-THC when exposed to heat or light, and it is often consumed in its raw form for its potential health benefits. Some research suggests that THC-A may have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, although more research is needed to understand its potential uses.
THCV:
Tetrahydrocannabivarin, or THCV, is a minor cannabinoid found in cannabis that is believed to have potential therapeutic effects. THCV has been reported to have appetite suppressant and anticonvulsant properties, as well as potential uses in the treatment of diabetes and obesity. THCV works by interacting with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce its effects.
Synthetic Cannabinoids:
HHC:
HHC is a synthetic cannabinoid that is similar in structure to THC, but it has been modified to produce different effects on the body. It is often marketed as a legal alternative to THC, although its legal status may vary depending on the jurisdiction.
THC-O:
THC-O (tetrahydrocannabinol-o-acetate) is a synthetic cannabinoid that is more potent than delta-9 THC. It is typically synthesized from other cannabinoids such as delta-8 or delta-9 THC, and it has been reported to produce more intense and longer-lasting effects than other cannabinoids.
THC-P:
THC-P (tetrahydrocannabinol-pentyl) is another synthetic cannabinoid that is more potent than delta-9 THC. It is made from a chemical precursor and has been reported to produce stronger and longer-lasting effects than other cannabinoids.
SUMMARY:
In conclusion, cannabinoids are a group of chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce a range of effects on the body and mind.
While research on cannabinoids is still in its early stages, there is growing evidence to suggest that these compounds may have potential therapeutic applications for a range of health conditions.
It’s important to note that while some of these cannabinoids may have different effects or levels of potency compared to delta-9 THC, they are all still considered to be psychoactive and can produce similar effects on the body and mind.
And, while there is vastly growing interest, research and ongoing testing on the therapeutic applications of cannabinoids, it is still important to note that the legal status of cannabis and cannabinoids varies widely from state to state, and country to country.
Before diving into personal use of use of these compounds, be sure to check the legal status of cannabis and cannabinoids in your jurisdiction before using them.